The MEG team at the Deloitte 2025 Technology Fast 50 Awards
Dublin, Ireland, 27th November 2025 – MEG has been recognised as one of Ireland’s fastest-growing technology companies for the second year running, securing the #21 position in the 2025 Deloitte Technology Fast 50 Awards. The company has risen three places since last year, reflecting sustained momentum and expanding impact across international healthcare markets.
MEG’s CEO, Kerrill Thornhill, credits the company’s progress to its commitment to customer-centred innovation and its growing global client base. He said,
“This recognition reflects the trust our healthcare partners place in us and the work our team puts into building technology that genuinely improves care quality, safety and patient outcomes. As healthcare systems face increasing complexity, we are proud to support organisations with solutions that make care safer, more consistent and more transparent.”
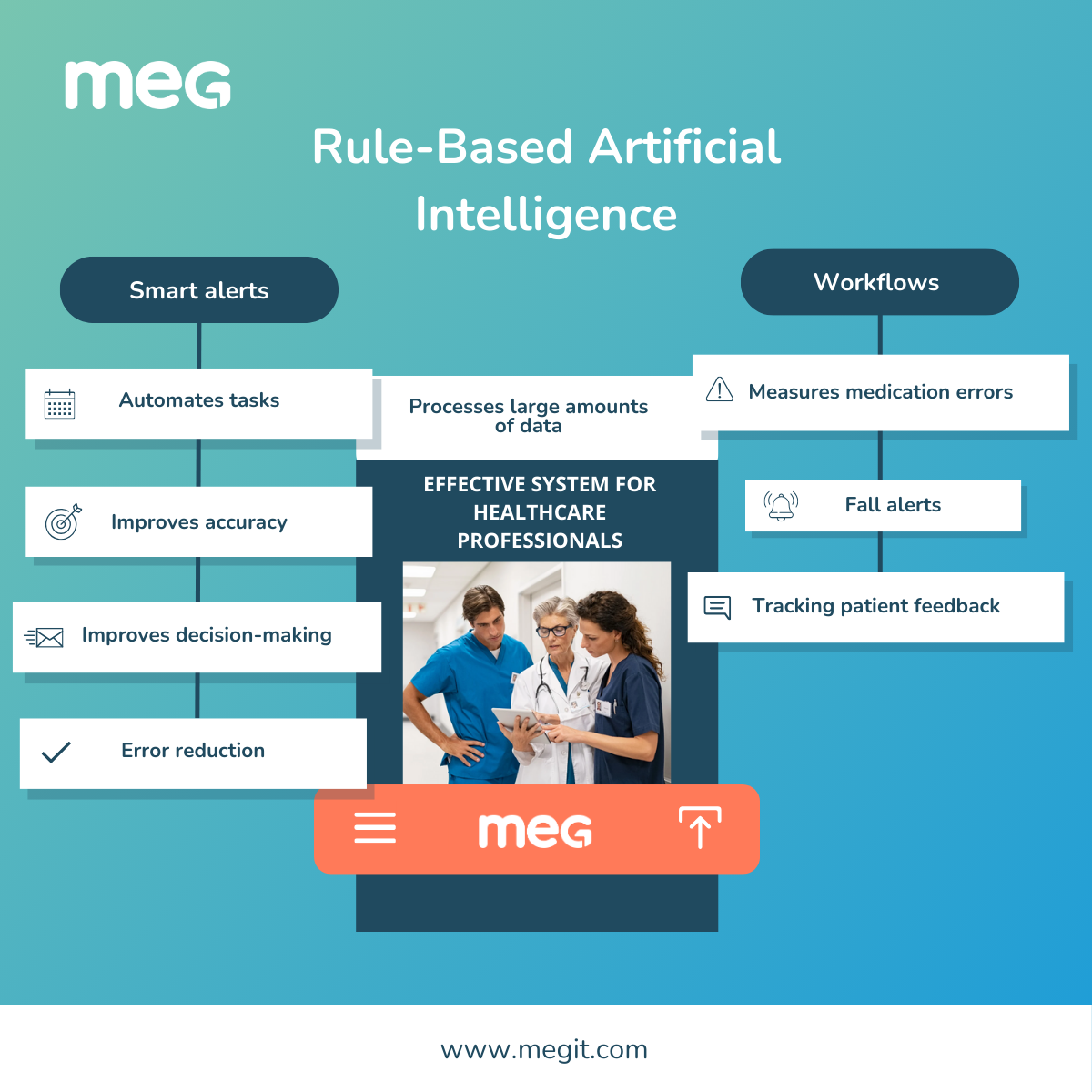
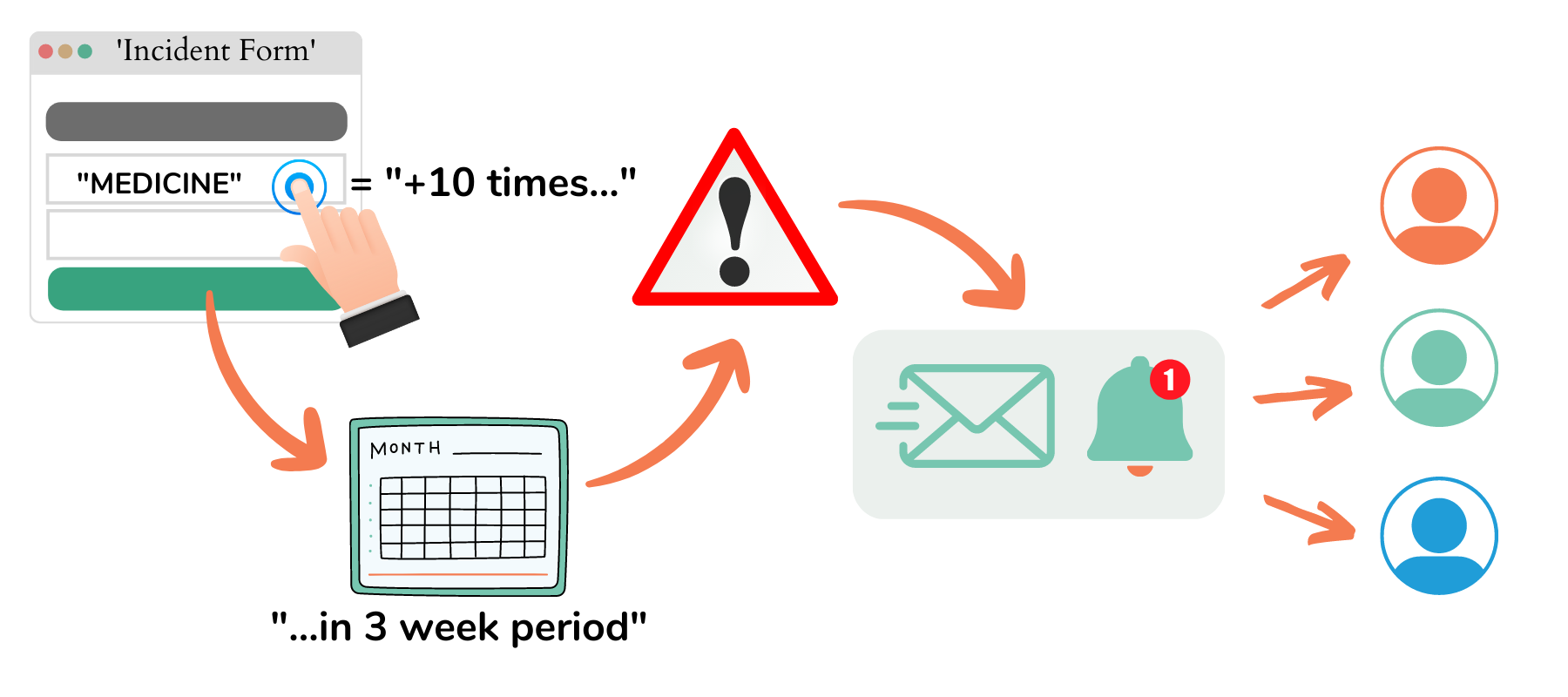
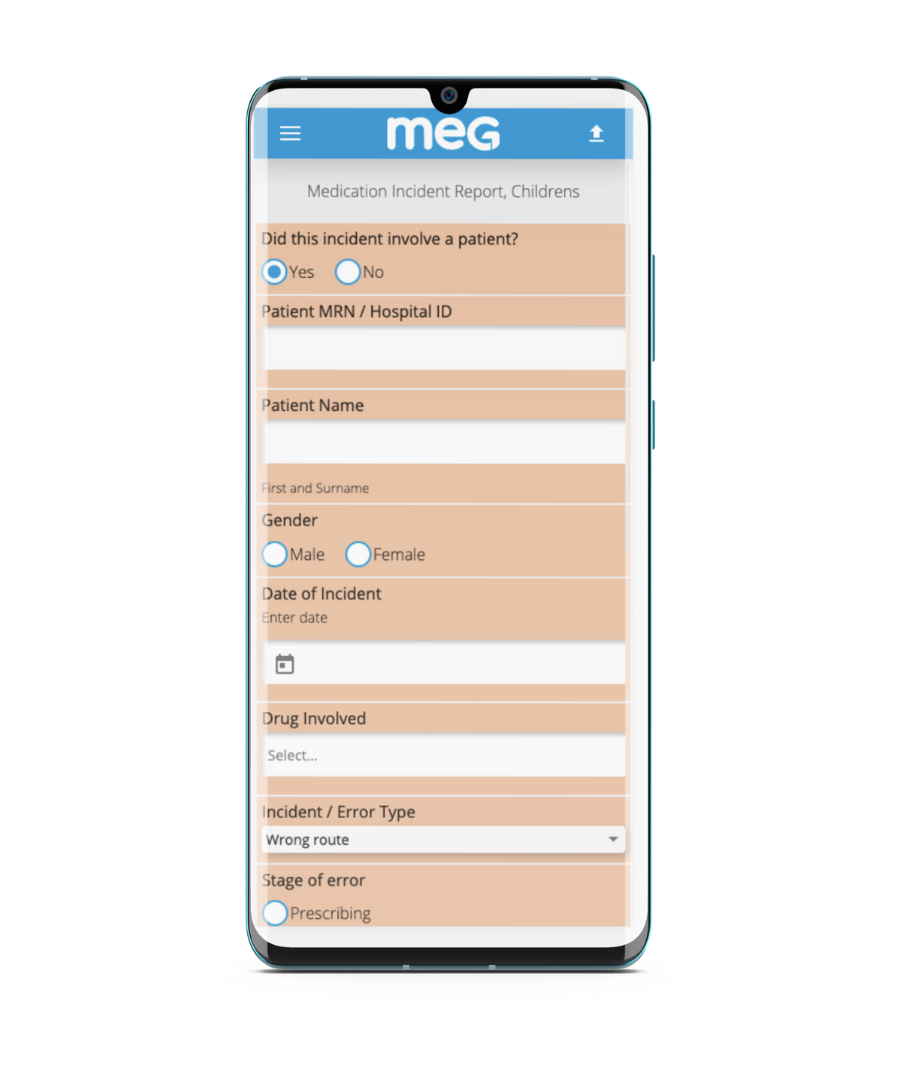
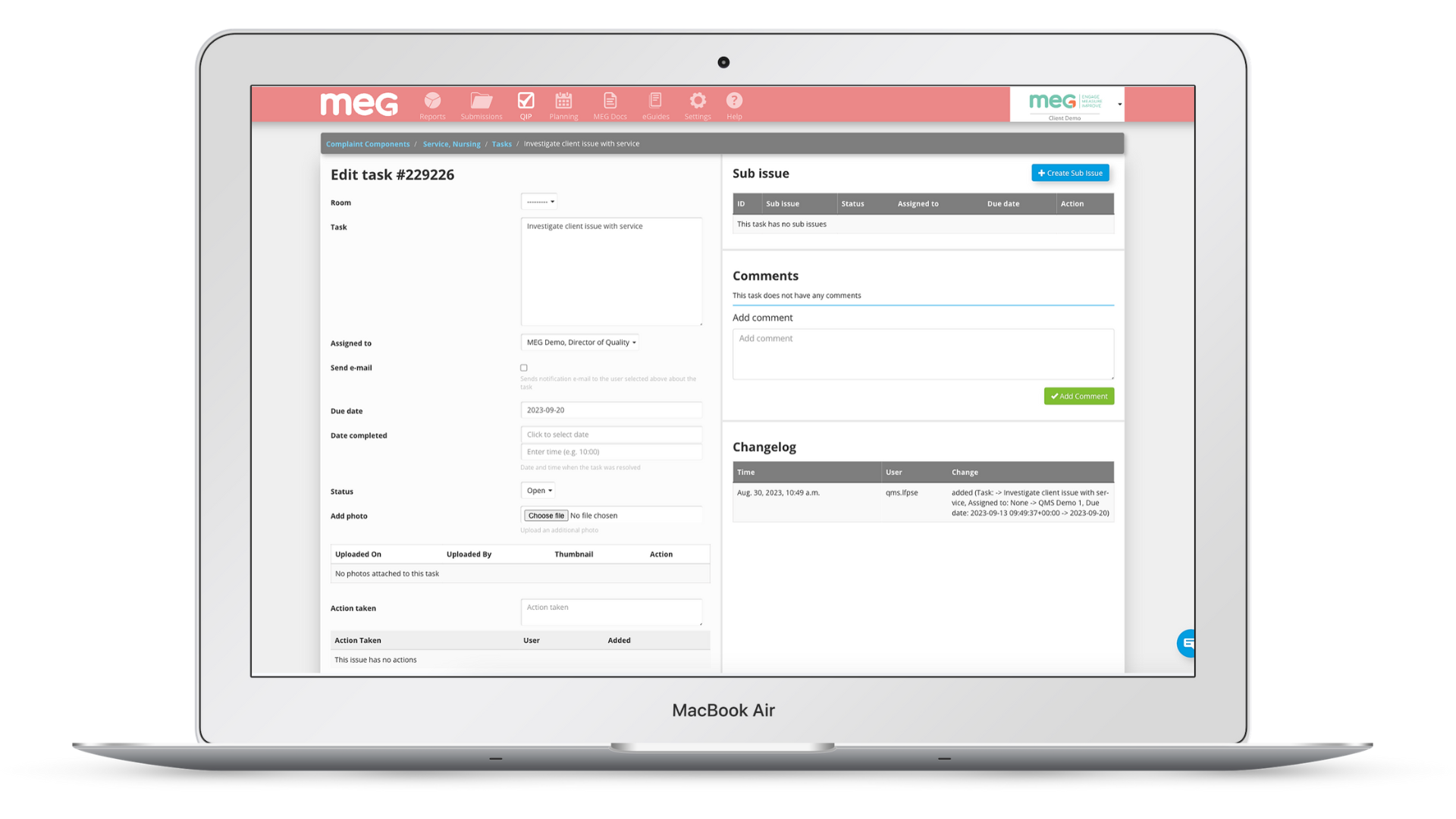
MEG continues to grow across Europe, the Middle East, North & South America and Asia-Pacific supporting hospitals and health systems with an end-to-end quality management platform that centralises real-time auditing, incident oversight, document management, governance processes and improvement activity in one unified system.
The Deloitte Technology Fast 50 Awards rank the 50 fastest-growing technology companies in Ireland based on four-year revenue growth. The 2025 cohort collectively generated €1.76 billion in annual revenues and employed more than 7,600 people. This year’s ranking highlights the continued strength of Ireland’s indigenous tech sector, now in its 26th year of recognition.
This year’s result also highlights the increasing influence of artificial intelligence in driving growth. Commenting on this year’s results, James Toomey, Partner and Fast 50 Lead at Deloitte, said:
“A standout from this year’s awards is that companies with Artificial Intelligence (AI) embedded in their operations are seeing the biggest growth, but access to skilled employees who can prompt and deploy AI effectively will be crucial.”
MEG expressed its gratitude to its team, customers and partners for their continued support, noting that the company’s achievements are the result of shared commitment and collaboration. MEG also extended its thanks to Deloitte Ireland for this recognition and congratulated all organisations included in the 2025 Fast 50 ranking.
About MEG
MEG is a digital quality management system for healthcare. Its suite of configurable mobile and cloud-based tools enables providers to engage staff in quality improvement, patient safety, and manage compliance with accreditation or regulatory standards. The easy-to-use modules can be used by frontline workers on any device to collect data from all over an organisation. They can capture incidents, conduct audits, risk assessments, feedback surveys, and access documents and information anytime at the point of care. Management can collate, analyse and act upon real-time information and metrics across multiple sites, consolidating data into a centralised platform. MEG operates in more than 30 countries in Europe, the Middle East, Australasia, and Latin America and offers multilingual support.